Diagnosis
Your healthcare professional asks about your medical history and does a physical exam. A thorough medical history and physical exam can give important clues about a chronic cough. Your health professional also may order tests to look for the cause of your chronic cough.
But many health professionals start treatment for one of the common causes of chronic cough rather than ordering expensive tests. If the treatment doesn't work, you may be tested for less common causes.
Imaging tests
- X-rays. Although a routine chest X-ray won't reveal the most common reasons for a cough — postnasal drip, acid reflux, tobacco use or asthma — it may be used to check for lung cancer, pneumonia and other lung diseases. An X-ray of your sinuses may reveal evidence of a sinus infection.
- Computerized tomography scans. These scans also are called CT scans. They may be used to check your lungs for conditions that may produce chronic cough or your sinus cavities for pockets of infection.
Lung function tests
Spirometer
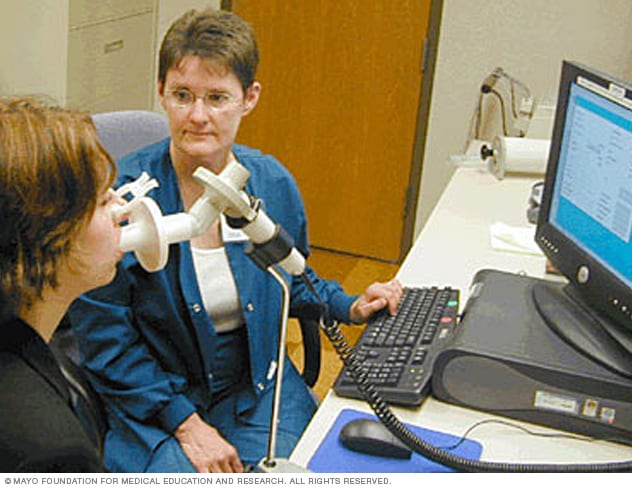
Spirometer
A spirometer is a diagnostic device that measures the amount of air you can breathe in and out and the time it takes you to breathe out completely after you take a deep breath.
These simple, noninvasive tests, such as spirometry, are used to diagnose asthma and COPD. They measure how much air your lungs can hold and how fast you can exhale.
Your healthcare professional may request an asthma challenge test. This test checks how well you can breathe before and after inhaling the drug methacholine (Provocholine).
Lab tests
If the mucus that you cough up is colored, your healthcare professional may want to test a sample of it for bacteria.
Scope tests
If your healthcare professional can't find the cause of your cough, special scope tests may be used to look for possible causes. These tests may include:
- Bronchoscopy. A bronchoscope is a thin, flexible tube that has a light and camera attached to it. Your health professional can look at your lungs and air passages. A biopsy also can be taken from the inside lining of your airway, also known as the mucosa, to look for anything unusual. A biopsy is a procedure to remove a sample of tissue for testing in a lab.
- Rhinoscopy. Using a fiberoptic scope, also known as a rhinoscope, your health professional can view your nasal passageways, sinuses and upper airway.
Children
A chest X-ray and spirometry, at a minimum, are usually ordered to find the cause of a chronic cough in children.
More Information
Treatment
Finding out what's causing a chronic cough is very important to effective treatment. In many cases, more than one underlying condition may be causing your chronic cough.
If you smoke, your healthcare professional likely will talk with you about your readiness to quit and give you advice on how to achieve this goal. If you're taking an ACE inhibitor medicine, your health professional may switch you to another medicine that doesn't have cough as a side effect.
Medicines used to treat chronic cough may include:
- Antihistamines, corticosteroids and decongestants. These medicines are standard treatment for allergies and postnasal drip.
- Inhaled asthma medicines. The most effective treatments for asthma-related cough are corticosteroids and bronchodilators. They reduce inflammation and open up your airways.
- Antibiotics. If a bacterial, fungal or mycobacterial infection is causing your chronic cough, your healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotic medicines for the infection.
- Acid blockers. When lifestyle changes don't take care of acid reflux, you may be treated with medicines that block acid production. Some people need surgery to resolve the problem.
Medicine to reduce coughing
Your healthcare professional works to find the cause of your cough and the best treatment for you. During that time, your healthcare professional also may prescribe a medicine to reduce coughing, called a cough suppressant. Cough suppressants are not recommended for children.
Cough and cold medicines available without a prescription treat the symptoms of coughs and colds — not the underlying disease. Research suggests that these medicines don't work any better than no medicine at all. These medicines are not recommended for children because of potentially serious side effects, including fatal overdoses in children younger than 2 years old.
Don't use over-the-counter cough and cold medicines, except for fever reducers and pain relievers, to treat coughs and colds in children younger than 6 years old. Also, avoid use of these medicines for children younger than 12 years old. Check with your healthcare professional for guidance.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Follow the plan your healthcare professional gives you for treating the cause of your cough. In the meantime, you can try these tips to ease your cough:
- Drink fluids. Liquid helps thin the mucus in your throat. Warm liquids, such as broth, tea or juice, can soothe your throat.
- Suck on cough drops or hard candies. They may ease a dry cough and soothe an irritated throat.
- Consider taking honey. A teaspoon of honey may help loosen a cough. Don't give honey to children younger than 1 year old. Honey can contain bacteria harmful to infants.
- Moisturize the air. Use a cool-mist humidifier or take a steamy shower.
- Avoid tobacco smoke. Smoking or breathing secondhand smoke irritates your lungs and can worsen coughs. If you smoke, talk with your healthcare professional about programs and products that can help you quit.
Preparing for your appointment
You may see your family healthcare professional at first. But you may need to see a doctor who specializes in lung disorders. This health professional is known as a pulmonologist.
What you can do
Before your appointment, make a list that includes:
- Detailed descriptions of your symptoms.
- Information about medical problems you've had.
- Information about the medical problems of your parents or siblings.
- All the medicines, including those available without a prescription, vitamins, herbal preparations and dietary supplements you take.
- Your smoking history.
- Questions you want to ask the healthcare professional.
What to expect from your doctor
Your healthcare professional may ask some of these questions:
- What are your symptoms and when did they begin?
- Did you recently have the flu or a cold?
- Do you smoke tobacco or have you ever smoked tobacco?
- Does anyone in your family or workplace smoke?
- Are you exposed to dust or chemicals at home or at work?
- Do you have heartburn?
- Do you cough up anything? If so, what does it look like?
- Do you take blood pressure medicine? If so, what type do you take?
- When does your cough occur?
- Does anything relieve your cough? What treatments have you tried?
- Do you get short of breath or wheeze when you move around or when exposed to cold air?
- What is your travel history?
Your healthcare professional will ask more questions based on your responses, symptoms and needs. Preparing for questions will help you make the most of your time.
Oct. 29, 2024