Diagnosis
It's important to determine the type of urinary incontinence that you have, and your symptoms often tell your doctor which type you have. That information will guide treatment decisions.
Your doctor is likely to start with a thorough history and physical exam. You may then be asked to do a simple maneuver that can demonstrate incontinence, such as coughing.
After that, your doctor will likely recommend:
- Urinalysis. A sample of your urine is checked for signs of infection, traces of blood or other abnormalities.
- Bladder diary. For several days you record how much you drink, when you urinate, the amount of urine you produce, whether you had an urge to urinate and the number of incontinence episodes.
- Postvoid residual measurement. You're asked to urinate (void) into a container that measures urine output. Then your doctor checks the amount of leftover urine in your bladder using a catheter or ultrasound test. A large amount of leftover urine in your bladder may mean that you have an obstruction in your urinary tract or a problem with your bladder nerves or muscles.
If further information is needed, your doctor may recommend more-involved tests, such as urodynamic testing and pelvic ultrasound. These tests are usually done if you're considering surgery.
More Information
Treatment
Treatment for urinary incontinence depends on the type of incontinence, its severity and the underlying cause. A combination of treatments may be needed. If an underlying condition is causing your symptoms, your doctor will first treat that condition.
Your doctor may recommend less invasive treatments to start with and move on to other options if these techniques fail to help you.
Behavioral techniques
Your doctor may recommend:
- Bladder training, to delay urination after you get the urge to go. You may start by trying to hold off for 10 minutes every time you feel an urge to urinate. The goal is to lengthen the time between trips to the toilet until you're urinating only every 2.5 to 3.5 hours.
- Double voiding, to help you learn to empty your bladder more completely to avoid overflow incontinence. Double voiding means urinating, then waiting a few minutes and trying again.
- Scheduled toilet trips, to urinate every two to four hours rather than waiting for the need to go.
- Fluid and diet management, to regain control of your bladder. You may need to cut back on or avoid alcohol, caffeine or acidic foods. Reducing liquid consumption, losing weight or increasing physical activity also can ease the problem.
Pelvic floor muscle exercises
Female pelvic floor muscles
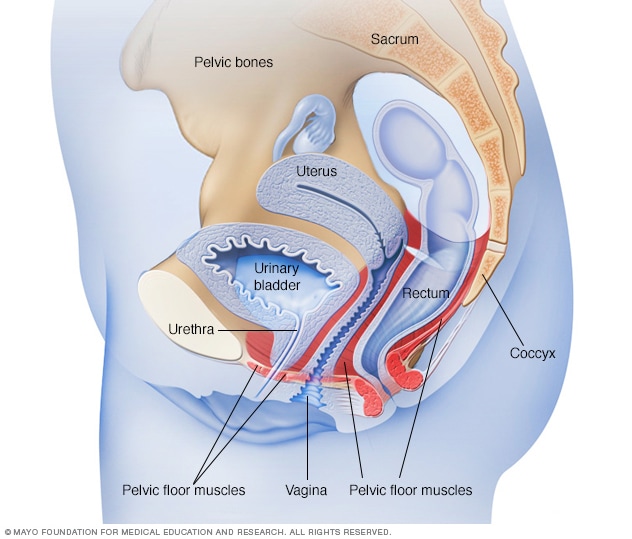
Female pelvic floor muscles
The pelvic floor muscles support the pelvic organs. Those organs include the uterus, bladder and rectum. Kegel exercises can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles.
Male pelvic floor muscles
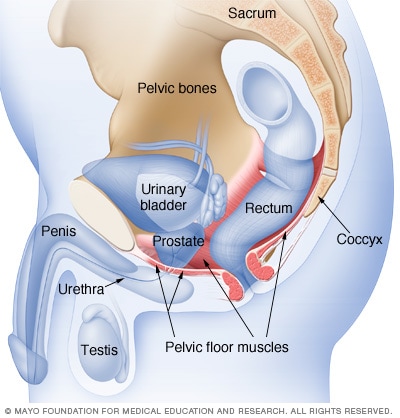
Male pelvic floor muscles
The male pelvic floor muscles support the bladder and bowel and affect sexual function. Kegel exercises can help strengthen these muscles.
Your doctor may recommend that you do these exercises frequently to strengthen the muscles that help control urination. Also known as Kegel exercises, these techniques are especially effective for stress incontinence but may also help urge incontinence.
To do pelvic floor muscle exercises, imagine that you're trying to stop your urine flow. Then:
- Tighten (contract) the muscles you would use to stop urinating and hold for five seconds, and then relax for five seconds. (If this is too difficult, start by holding for two seconds and relaxing for three seconds.)
- Work up to holding the contractions for 10 seconds at a time.
- Aim for at least three sets of 10 repetitions each day.
To help you identify and contract the right muscles, your doctor may suggest that you work with a pelvic floor physical therapist or try biofeedback techniques.
Medications
Medications commonly used to treat incontinence include:
- Anticholinergics. These medications can calm an overactive bladder and may be helpful for urge incontinence. Examples include oxybutynin (Ditropan XL), tolterodine (Detrol), darifenacin (Enablex), fesoterodine (Toviaz), solifenacin (Vesicare) and trospium chloride.
- Mirabegron (Myrbetriq). Used to treat urge incontinence, this medication relaxes the bladder muscle and can increase the amount of urine your bladder can hold. It may also increase the amount you are able to urinate at one time, helping to empty your bladder more completely.
- Alpha blockers. In men who have urge incontinence or overflow incontinence, these medications relax bladder neck muscles and muscle fibers in the prostate and make it easier to empty the bladder. Examples include tamsulosin (Flomax), alfuzosin (Uroxatral), silodosin (Rapaflo), and doxazosin (Cardura).
- Topical estrogen. Applying low-dose, topical estrogen in the form of a vaginal cream, ring or patch may help tone and rejuvenate tissues in the urethra and vaginal areas.
Electrical stimulation
Electrodes are temporarily inserted into your rectum or vagina to stimulate and strengthen pelvic floor muscles. Gentle electrical stimulation can be effective for stress incontinence and urge incontinence, but you may need multiple treatments over several months.
Medical devices
Types of pessaries
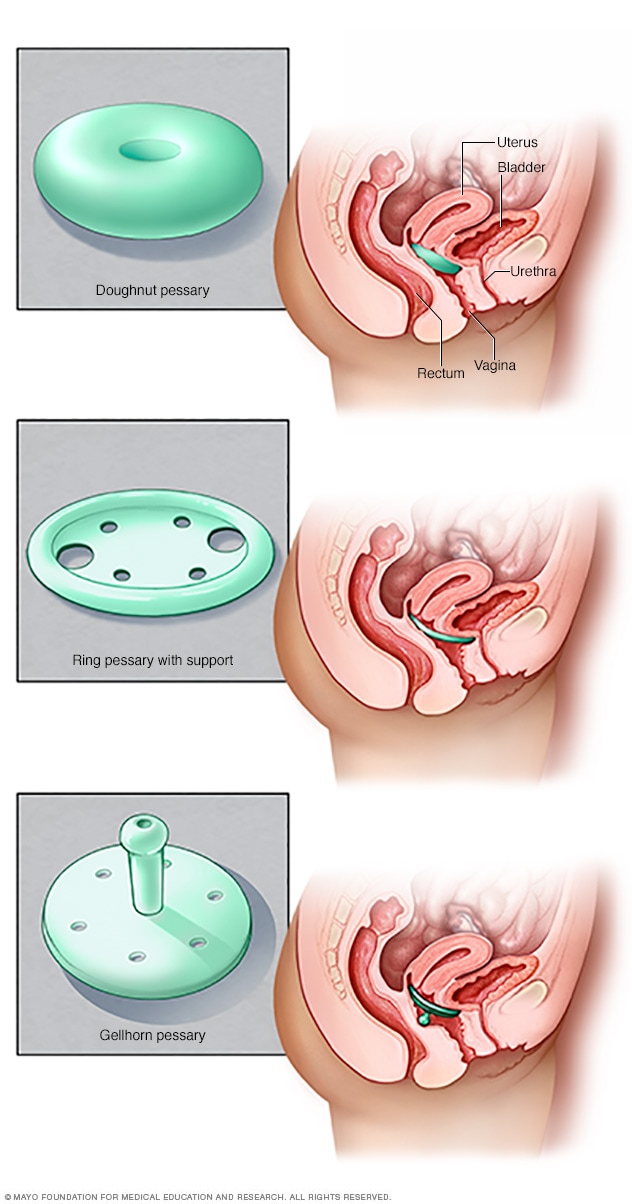
Types of pessaries
Pessaries come in many shapes and sizes. The device fits into the vagina and provides support to vaginal tissues displaced by pelvic organ prolapse. A health care provider can fit a pessary and help provide information about which type would work best.
Devices designed to treat women with incontinence include:
- Urethral insert, a small, tampon-like disposable device inserted into the urethra before a specific activity, such as tennis, that can trigger incontinence. The insert acts as a plug to prevent leakage and is removed before urination.
- Pessary, a flexible silicone ring that you insert into your vagina and wear all day. The device is also used in women with vaginal prolapse. The pessary helps support the urethra, to prevent urine leakage.
Interventional therapies
Sacral nerve stimulator
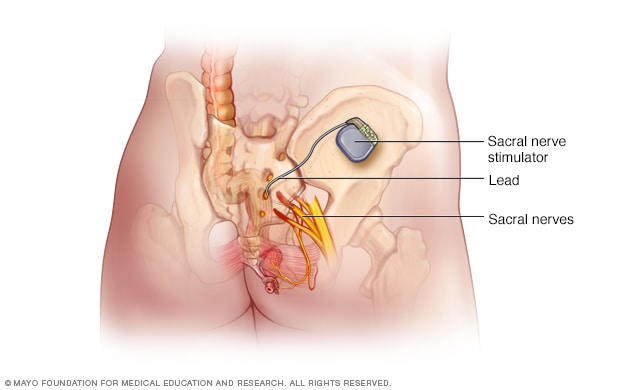
Sacral nerve stimulator
During sacral nerve stimulation, a surgically implanted device delivers electrical impulses to the nerves that regulate bladder activity. These are called the sacral nerves. The unit is placed under the skin in the lower back, about where the back pocket is on a pair of pants. In this image, the device is shown out of place to allow a better view of the unit.
Interventional therapies that may help with incontinence include:
- Bulking material injections. A synthetic material is injected into tissue surrounding the urethra. The bulking material helps keep the urethra closed and reduce urine leakage. This procedure is for the treatment of stress incontinence and is generally less effective than more-invasive treatments such as surgery. It may need to be repeated more than once.
- OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox). Injections of Botox into the bladder muscle may benefit people who have an overactive bladder and urge incontinence. Botox is generally prescribed to people only if other treatments haven't been successful.
- Nerve stimulators. There are two types of devices that use painless electrical pulses to stimulate the nerves involved in bladder control (sacral nerves). One type is implanted under your skin in your buttock and connected to wires on the lower back. The other type is a removable plug that is inserted into the vagina. Stimulating the sacral nerves can control overactive bladder and urge incontinence if other therapies haven't worked.
Surgery
Bladder neck suspension
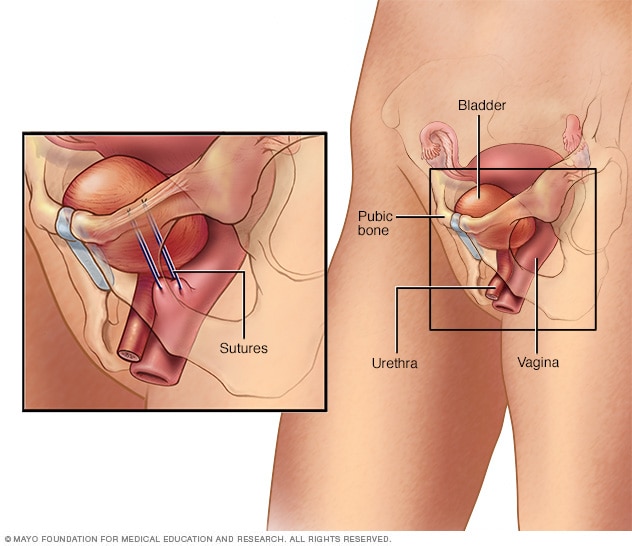
Bladder neck suspension
The Burch procedure, the most common suspension surgery, adds support to the bladder neck and urethra, reducing the risk of stress incontinence. In this version of the procedure, surgery involves placing sutures in vaginal tissue near the neck of the bladder — where the bladder and urethra meet — and attaching them to ligaments near the pubic bone.
If other treatments aren't working, several surgical procedures can treat the problems that cause urinary incontinence:
- Sling procedures. Synthetic material (mesh) or strips of your body's tissue are used to create a pelvic sling underneath your urethra and the area of thickened muscle where the bladder connects to the urethra (bladder neck). The sling helps keep the urethra closed, especially when you cough or sneeze. This procedure is used to treat stress incontinence.
- Bladder neck suspension. This procedure is designed to provide support to your urethra and bladder neck — an area of thickened muscle where the bladder connects to the urethra. It involves an abdominal incision, so it's done during general or spinal anesthesia.
- Prolapse surgery. In women who have pelvic organ prolapse and mixed incontinence, surgery may include a combination of a sling procedure and prolapse surgery. Repair of pelvic organ prolapse alone does not routinely improve urinary incontinence symptoms.
- Artificial urinary sphincter. A small, fluid-filled ring is implanted around the bladder neck to keep the urinary sphincter shut until there's a need to urinate. To urinate, you press a valve implanted under your skin that causes the ring to deflate and allows urine from your bladder to flow.
Absorbent pads and catheters
If medical treatments can't eliminate your incontinence, you can try products that help ease the discomfort and inconvenience of leaking urine:
- Pads and protective garments. Most products are no more bulky than normal underwear and can be easily worn under everyday clothing. Men who have problems with dribbles of urine can use a drip collector — a small pocket of absorbent padding that's worn over the penis and held in place by close-fitting underwear.
- Catheter. If you're incontinent because your bladder doesn't empty properly, your doctor may recommend that you learn to insert a soft tube (catheter) into your urethra several times a day to drain your bladder. You'll be instructed on how to clean these catheters for safe reuse.
More Information
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Problems with urine leakage may require you to take extra care to prevent skin irritation:
- Use a washcloth to clean yourself.
- Allow your skin to air-dry.
- Avoid frequent washing and douching because these can overwhelm your body's natural defenses against bladder infections.
- Consider using a barrier cream, such as petroleum jelly or cocoa butter, to protect your skin from urine.
- Ask your doctor about special cleansers made to remove urine that may be less drying than other products.
If you have urge incontinence or nighttime incontinence, make the toilet more convenient:
- Move any rugs or furniture you might trip over or collide with on the way to the toilet.
- Use a night light to illuminate your path and reduce your risk of falling.
If you have functional incontinence, you might:
- Keep a bedside commode in your bedroom
- Install an elevated toilet seat
- Widen an existing bathroom doorway
Alternative medicine
There are no alternative medicine therapies that have been proved to cure urinary incontinence. Early studies have shown that acupuncture can provide some benefit. Yoga also may provide some benefit for urinary incontinence, but more study is needed.
Coping and support
If you're embarrassed about a bladder control problem, you may try to cope on your own by wearing absorbent pads, carrying extra clothes or even avoiding going out.
But effective treatments are available for urinary incontinence. It's important to ask your doctor about treatment. Once you do, you'll be on your way to regaining an active and confident life.
Preparing for your appointment
If you have urinary incontinence, you're likely to start by seeing your primary care doctor. You may be referred to a doctor who specializes in urinary tract disorders (urologist) or a gynecologist with special training in female bladder problems and urinary function (urogynecologist).
What you can do
To get ready for your appointment, it helps to:
- Be aware of any pre-appointment restrictions, such as restricting your diet
- Write down your symptoms, including how often you urinate, nighttime bladder activity and episodes of incontinence
- Make a list of all your medications, vitamins and supplements, including doses and how often you take the medication
- Write down key medical information, including other conditions you may have
- Ask a relative or friend to accompany you, to help you remember what the doctor says
- Take a notebook or electronic device with you, and use it to note important information during your visit
- Write down questions to ask your doctor
For urinary incontinence, some basic questions to ask your doctor include:
- What's the most likely cause of my symptoms?
- What kinds of tests do I need? Do these tests require any special preparation?
- Is my urinary incontinence temporary?
- What treatments are available?
- Should I anticipate any side effects of the treatment?
- Is there a generic alternative to the medicine you're prescribing for me?
- I have other health conditions. How can I best manage these conditions together?
Don't hesitate to ask other questions during your appointment as they occur to you.
What to expect from your doctor
Your doctor is likely to ask you a few questions, such as:
- When did you first begin experiencing symptoms, and how severe are they?
- Have your symptoms been continuous or occasional?
- What, if anything, seems to improve or worsen your symptoms?
- How often do you need to urinate?
- When do you leak urine?
- Do you have trouble emptying your bladder?
- Have you noticed blood in your urine?
- Do you smoke?
- How often do you drink alcohol and caffeinated beverages?
- How often do you eat spicy, sugary or acidic foods?
Feb. 09, 2023