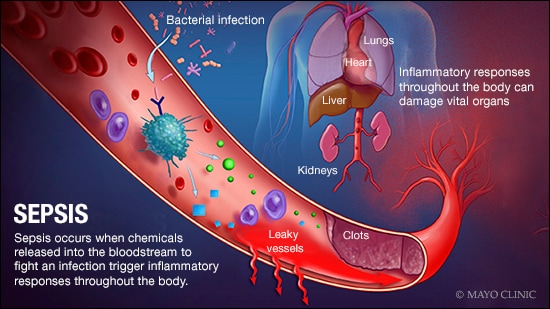
诊断
医生通常会安排进行多次检查,以查明潜在的感染。
血液检测
使用血样来检测:
- 感染的证据。
- 凝血问题。
- 肝脏或肾脏功能异常。
- 氧气含量较低,不能满足身体需求。
- 电解质失衡。
其他化验
其他用于确定感染源的化验可能包括:
- 尿液。
- 伤口流出的液体。
- 呼吸道黏液和唾液。
影像学检查
如果感染部位不容易找到,医务人员可能会安排更多检查。影像学检查的一些示例包括:
- X 线检查。X 线检查可以显示肺部感染情况。
- 超声检查。这种机器使用声波在显示屏上生成实时影像。超声检查可显示膀胱和肾脏感染情况。
- 计算机断层成像(CT)。这种机器可从各种角度拍摄 X 线影像,并将这些 X 线影像结合起来形成身体内部结构的横截面切片。肝脏、胰腺或其他腹部器官感染通过 CT 扫描更容易看到。
- 磁共振成像(MRI)。这种机器使用无线电波和强磁体来生成横截面或 3D 影像,有助于查看软组织或骨感染。
治疗
早期的全面治疗可增加康复的可能性。脓毒症患者需要在医院重症监护室接受严密监测和治疗。这是因为脓毒症患者可能需要采取挽救生命的措施来稳定呼吸和心脏活动。
药物
有多种不同的药物可以治疗脓毒症和感染性休克。其中包括:
- 抗生素。尽快开始使用抗生素治疗。一般先使用广谱抗生素,这类药物对多种细菌有效。通过血液测试查明引起感染的具体细菌类型后,可能从第一种抗生素换成另一种。第二种抗生素将靶向引起感染的细菌。
- 静脉输液。尽快开始静脉输液。
- 血管加压药。血管加压药可使血管收缩,有助于增加血压。如果输液后血压仍然过低,可以使用血管加压药。
也可以使用其他药物,例如用于调整血糖水平的胰岛素或止痛药。
支持性护理
脓毒症患者经常接受输氧等支持性护理。有些人可能需要使用呼吸机以帮助通气。如果感染同时造成肾功能异常,患者可能需要进行透析。
外科手术
手术可能有助于消除感染源,例如脓液、感染组织或坏死组织。
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.