Overview
Breast reconstruction with implants is surgery that restores shape to the breast using a breast implant. This surgery most often is done after a mastectomy to treat or prevent breast cancer. A mastectomy is surgery to remove all breast tissue from a breast.
Breast reconstruction with implants uses breast implants to reshape the breasts. The implants are made of silicone and typically are filled with silicone gel. A plastic surgeon does this complex procedure.
Breast reconstruction with implants typically starts at the time of the mastectomy. Often it is a process that may need two or more operations to complete.
The goal of breast reconstruction is to give you the most natural look and feel possible after breast cancer surgery. Some people say having breast reconstruction improves their confidence and the comfort they feel with their bodies. Others say their new breast helps them feel whole and gives them a more positive outlook. But breast reconstruction can't replace your breast exactly. The new breast may not look or feel the same or have the same sensations as a natural breast.
Why it's done
Breast reconstruction with implants is done to restore shape to a breast after a mastectomy. Many people choose breast reconstruction after mastectomy to feel better about themselves and how they look.
There are two main kinds of breast reconstruction. One uses implants and the other uses tissue flaps. Breast reconstruction with flap surgery uses tissue from another part of your body to reconstruct the breast.
The ways of doing breast reconstruction surgery each have advantages and disadvantages. A plastic surgeon can talk about these with you.
In general, using an implant for breast reconstruction is a less invasive operation compared to reconstruction with a tissue flap. Reconstruction with an implant may offer a faster recovery. But breast implants aren't designed to last forever. If your breast reconstruction uses implants, you may need more surgery in the future to replace or remove the implant. If you choose flap surgery for breast reconstruction, you typically won't need more surgery in the future.
Talk with a plastic surgeon about your options. The surgeon can help you choose which type of reconstruction is better for you.
Risks
Breast reconstruction with implants carries a risk of complications. Complications may be related to the surgery or to the implant.
Risks of surgery
The risks of breast reconstruction surgery include:
- Slow healing of cuts in the skin, called incisions.
- Infection.
- Bleeding.
- Risks linked to the medicine that puts you in a sleeplike state during surgery. The medicine is called a general anesthetic. Risks include nausea, vomiting and confusion.
Risks of having implants
The risks of having breast implants include:
- Breasts that don't match each other in size or how they look, called asymmetry.
- Breast pain.
- Implant leaks or tears.
- Higher risk of future breast surgery to replace or remove the breast implant.
- Changes in feeling in the breast.
- Scar tissue that changes the shape of the breast implant, called capsular contracture.
- A slightly higher risk of a rare immune system cancer called anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Also called ALCL, it's linked with breast implants that have a textured surface. The link between breast implants and ALCL needs more study.
Treating these complications may mean more surgery to remove or replace the implants.
Breast reconstruction with implants might not be a good choice for you if you need radiation therapy to the skin and chest wall after mastectomy. There may be a higher risk of complications. Radiation therapy can cause skin changes that may lead to a higher risk of infection and problems with wound healing.
How you prepare
If you're thinking about breast reconstruction with implants, talk with a plastic surgeon about the surgery. Choose a plastic surgeon who is board certified and experienced in breast reconstruction after mastectomy. It's ideal if your breast cancer surgeon and the plastic surgeon work together. Then they can come up with the best surgical treatment and breast reconstruction plan for you.
Your plastic surgeon talks with you about your surgical choices and the pros and cons of implant-based reconstruction. You may see photos of people who have had different types of breast reconstruction.
Your body type, health and cancer treatment go into deciding which type of reconstruction will give you the best result. The plastic surgeon talks with you about where the surgery will take place and what follow-up procedures you might need.
Some people choose to have surgery on the other breast so that it matches the new breast. Ask your plastic surgeon about the pros and cons of having surgery on your other breast.
Your healthcare team may provide instructions about how to get ready for surgery. The instructions might include stopping or changing some medicines. The instructions also might say to quit smoking if you smoke. Smoking makes it harder for the body to heal after surgery. Follow your healthcare team's instructions carefully.
What you can expect
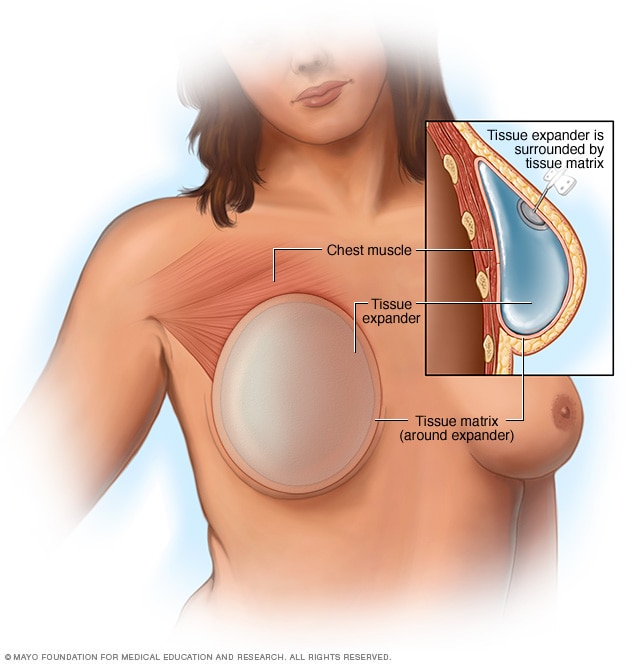
Tissue expander

Tissue expander
A tissue expander is a balloonlike device that helps stretch the chest skin and tissue to make room for a breast implant. A healthcare professional may slowly fill it with saline over a period of a few weeks to months. This picture shows the tissue expander under the chest muscle. The expander also can be placed on top of the chest muscle.
What you can expect depends on how you and your surgery team decide to do your reconstruction. Surgery to do breast reconstruction with implants often starts right after mastectomy surgery. Some people want to wait to have reconstruction surgery after they've healed from a mastectomy.
Ways that plastic surgeons can do breast reconstruction using implants include:
- Placing the breast implant right away. The plastic surgeon puts the breast implant in place once the breast surgeon completes the mastectomy.
- Placing a tissue expander right away. The plastic surgeon puts a balloonlike tissue expander in place once the breast surgeon completes the mastectomy. Surgery to put in a breast implant happens later.
- Doing the reconstruction later. If you don't want breast reconstruction right away, you can have this surgery later. Doing the reconstruction later may make it harder to get the most natural breast shape.
Placing the breast implant right away
Sometimes the plastic surgeon can place the breast implant at the time of the mastectomy. This is called direct-to-implant reconstruction.
While you are still in a sleeplike state, the plastic surgeon places the implant after the breast cancer surgeon has removed all the breast tissue. The plastic surgeon most often puts the implant above the chest muscle, also called the pectoral muscle. A breast implant is a round shell that's typically filled with silicone gel.
Placing the implant in front of the chest muscle is called a prepectoral breast implant. The implant sits just under the skin. Placing the implant under the chest muscle is called a subpectoral breast implant.
The plastic surgeon might use mesh or tissue called acellular dermal matrix to help hold the implant in place. Over time, the body replaces this tissue with its own cells.
Placing a tissue expander right away
Prepectoral breast implant
Prepectoral breast implant
A breast implant that's placed on top of the chest muscle is called a prepectoral breast implant. It's often done in two operations. First, a plastic surgeon places a balloonlike tissue expander under the skin. Over a period of a few weeks to months, a healthcare professional may slowly fill the expander with saline to the size you prefer. In a second operation, a plastic surgeon removes the expander and replaces it with a breast implant.
Most people having breast reconstruction with implants don't get breast implants right away. Instead, the plastic surgeon places a tissue expander in the chest. A tissue expander is like a balloon. A healthcare professional can slowly fill it over a few weeks to months.
As the tissue expander gets bigger, it slowly stretches the chest skin and tissue. This makes enough space on the chest to place a breast implant.
If you're having tissue expanders placed right away, the process starts just after your mastectomy surgery. While you're still in a sleeplike state, the plastic surgeon places the tissue expander. The surgeon may put the expander in front of the chest muscle or under the muscle.
After surgery you will return to see your healthcare team every week or two over the next months. A healthcare professional uses a needle to put saline into a small valve in the tissue expander. The valve is under your skin. Filling the expander slowly stretches the skin and tissue on the chest.
Once the expander makes enough room for an implant, you'll have another surgery. The plastic surgeon takes out the expander and replaces it with a breast implant. This might happen in 3 to 6 months if there's no need for radiation.
Doing the reconstruction surgery later
If you choose to wait to have breast reconstruction with an implant, the surgery most often starts with placing a tissue expander. The expander slowly stretches the skin and tissue on the chest. Then the plastic surgeon does another operation to take out the expander and replace it with an implant. Surgeons typically prefer to start reconstruction right away, rather than waiting. Doing the breast reconstruction later may make it harder to create the most natural breast shape.
After the procedure
After surgery, you may wear a stretchy bandage or support bra to keep swelling down and support the reconstructed breast. You may have a small tube under your skin for a time to drain blood or fluids. Your healthcare professional prescribes medicine to help manage your pain.
You may be tired and sore for several weeks after surgery. Getting back to usual activities takes time. Take it easy during this period.
You might need to restrict your activities. Follow your healthcare team's instructions on what activities are not OK. This may include not doing any overhead lifting or anything that could cause strain.
Contact your plastic surgeon right away if you have worries about your reconstruction.
Nipple reconstruction
Nipple reconstruction

Nipple reconstruction
After the breast has healed from reconstruction or mastectomy, a plastic surgeon can build a new nipple. The surgeon may make a star-shaped cut to form the new nipple. You also may choose to have a tattoo to recreate the circle of skin around the nipple, called the areola.
If your breast cancer surgery involved removing the nipple, you might think about surgery to create a new nipple. Surgery to make a new nipple is called nipple reconstruction. The plastic surgeon might make the new nipple with some of your skin. You might choose to have a tattoo applied to the nipple and to the circle of skin around it, called the areola.
Most often, a plastic surgeon does nipple reconstruction after you've healed from the implant surgery. But some people might have nipple reconstruction at the same time as the implant surgery.
Future breast cancer screening
If you have only one breast reconstructed, continue with mammograms for breast cancer screening on your other breast. You typically don't need mammograms on breasts that are reconstructed.
Continue to do breast self-exams on your natural breast and the skin and area around your reconstructed breast. Tell your healthcare professional about any changes you find.
Results
The results of breast reconstruction with implants might not be clear right away. It takes time for the tissue on your chest to heal. As your chest heals, you'll likely meet with your surgery team to talk about the results.
The goal of breast reconstruction is to give you the most natural look and feel possible after breast surgery. But breast reconstruction can't make your breast look or feel the same as it did before cancer. It is important to be realistic about what you can expect from breast reconstruction.
What breast reconstruction can do:
- Give your breast a shape.
- Help your breasts look more alike under clothing or in a bathing suit.
- Help you avoid needing to put a breast-shaped form, called a prosthesis, inside your bra.
What breast reconstruction may do:
- Improve how you feel about yourself and your body.
- Take away some of the physical reminders of your cancer.
What breast reconstruction won't do:
- Make you look the same as before your mastectomy.
- Make your reconstructed breast have the same feelings that it had before surgery.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies of tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.
Feb. 06, 2025