Diagnosis
EEG brain activity
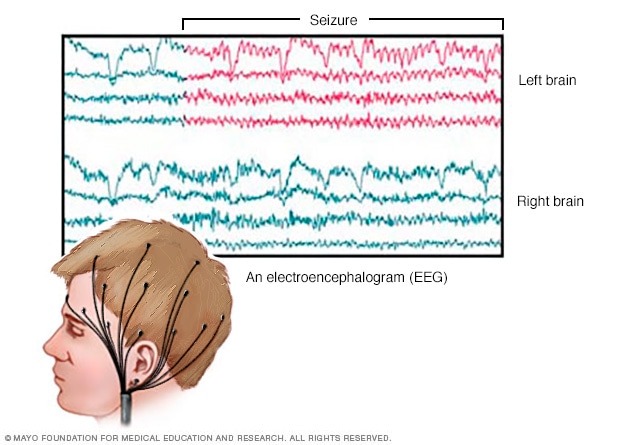
EEG brain activity
An EEG records the electrical activity of the brain through electrodes put on the scalp. EEG results show changes in brain activity. This may help diagnose brain conditions such as epilepsy and other seizure conditions.
High-density EEG

High-density EEG
During a high-density EEG, flat metal discs called electrodes are attached to the scalp. The electrodes are connected to the EEG machine with wires. Some people wear an elastic cap fitted with electrodes instead of having the adhesive put on their scalps.
CT scanner
CT scanner
A CT scan can show nearly all parts of the body. Healthcare professionals use it to diagnose disease or injury and to plan medical, surgical or radiation treatment.
Pinpointing seizure location
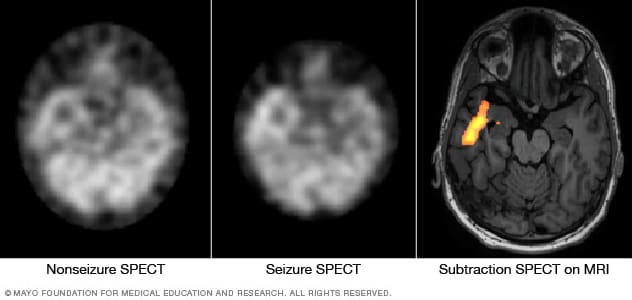
Pinpointing seizure location
These SPECT images show the blood flow in the brain when there's no seizure activity (left) and during a seizure (middle). The subtraction SPECT coregistered to MRI (right) helps pinpoint the area of seizure activity by overlapping the SPECT results with brain MRI results.
After a seizure, your healthcare professional reviews your symptoms and medical history and does a physical exam. You may have tests to find the cause of your seizure. Tests also may show how likely it is that you'll have another seizure.
Tests may include:
- A neurological exam. This is to look at your behavior, motor abilities and how your brain works.
- Blood tests. A blood sample can show blood sugar levels and look for signs of infections or gene conditions. A health professional also may check the levels of salts in the body that manage the balance of fluids. These salts are called electrolytes.
- A spinal tap. This procedure collects a sample of fluid from the spine for testing. Also called a lumbar puncture, a spinal tap may show whether an infection caused a seizure.
-
An electroencephalogram (EEG). In this test, electrodes are put on the scalp to record the electrical activity of the brain. The electrical activity shows up as wavy lines on an EEG recording. The EEG may show a pattern that tells whether a seizure is likely to happen again.
EEG testing also may help rule out other conditions that have symptoms like those of epilepsy. This test may be done at a clinic, overnight at home or over a few nights in the hospital.
Imaging tests may include:
- MRI. An MRI scan uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create a detailed view of the brain. An MRI may show changes in the brain that could lead to seizures.
- CT scan. A CT scan uses X-rays to get cross-sectional images of the brain. CT scans can show changes in the brain that might cause a seizure. Those changes may include tumors, bleeding and cysts.
- Positron emission tomography (PET). A PET scan uses a small amount of low-dose radioactive material that's put into a vein. The material helps show active areas of the brain and brain changes.
-
Single-photon emission computerized tomography (SPECT). A SPECT test uses a small amount of low-dose radioactive material that's put into a vein. The test creates a detailed 3D map of the blood flow in the brain that happens during a seizure.
A healthcare professional also may do a type of SPECT test called subtraction ictal SPECT coregistered with MRI (SISCOM). The test may give results with even more detail. This test is usually done in a hospital with overnight EEG recording.
An MRI is a very useful tool for helping your doctors see images of the inside of your body, including tissue that can't be seen on a conventional x-ray.
Before your exam, it's very important to fill out the safety screening form carefully. MRI is safe and painless. But metal in the scanner can cause serious safety problems or reduce the quality of the images.
Your health care team needs to know about any metal in your body, even a small shard of metal from an accident. Fillings, bridges, and other dental work typically do not pose a problem. But other metal that has been put into your body might prevent you from having an MRI. That includes some pacemakers, clips for treating aneurysms, and other devices with metal in them.
A nurse may review your health history before your exam. You may be given medications or contrast dye or have blood drawn. Be sure to tell the nurse if you're pregnant, have an allergy to contrast dye, or have kidney or liver problems. You may not wear clothing with snaps or zippers in the scanner. You will be asked to wear a gown. Do not wear any jewelry or bring anything metal into the scanner, including a hearing aid.
An MRI machine uses a powerful magnet to make images of your body. Unlike a CT scan, it does not use x-rays or other radiation. You will be given earplugs. The scanner makes a loud noise when it's operating.
A device called a coil may be put on or around the area to be scanned to help capture the images. You will also be given a squeeze ball to hold. You can use this to signal the technologist any time you need something. The MRI is controlled from a nearby room. You will be closely observed throughout the procedure.
A series of scans are taken with a brief pause between each. You may hear different noises as different scans are taken. It's normal for the noise to be very loud. You need to remain still when the scan is being taken.
People are typically in the scanner from 30 to 50 minutes, depending on the images to be taken. A complex examination can take longer. If you are concerned about being in the scanner for this length of time, talk to your physician and the technologist. They can help you with some tips for staying comfortable.
If you need to be removed from the scanner, this can be done very quickly. The ends of the scanner are always open.
After your exam, the images will be reviewed by your radiologist. He or she will send a report to the health care provider who ordered the test. Ask your health care provider any questions you have about your MRI.
More Information
Treatment
Implanted vagus nerve stimulation

Implanted vagus nerve stimulation
In vagus nerve stimulation, a device placed under the skin of the chest stimulates the vagus nerve in the neck. This sends signals to the brain that lessen seizures.
Deep brain stimulation
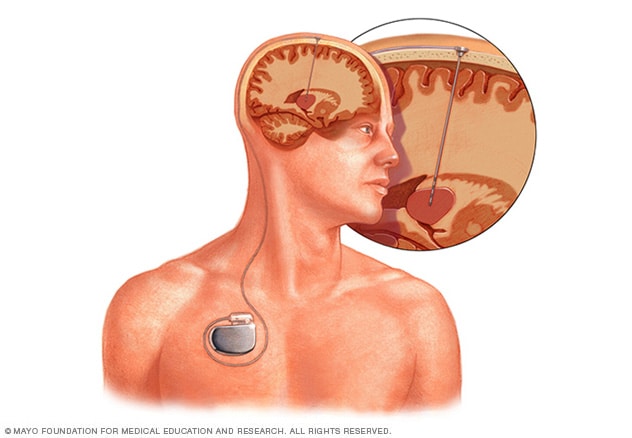
Deep brain stimulation
Deep brain stimulation involves putting an electrode deep within the brain. The amount of stimulation delivered by the electrode is controlled by a device placed under the skin in the chest. A wire that travels under the skin connects the device to the electrode.
Not everyone who has one seizure has another one. So your healthcare professional may not start treatment unless you've had more than one.
The goal in seizure treatment is to find the best therapy that stops seizures with the fewest side effects.
Medications
Treatment of seizures often involves antiseizure medicines. There are many types of antiseizure medicine.
Finding the right medicine and dosage can be hard. Some people try several medicines before finding the right one in the right dosage. Common side effects may include weight changes, dizziness, tiredness and mood changes. Very rarely, more-serious side effects can cause damage to the liver or bone marrow.
A healthcare professional thinks about your condition, how often you have seizures, your age and other factors when choosing which medicine to prescribe. The health professional also reviews other medicines you take to make sure that the antiseizure medicines won't interact with them.
Dietary therapy
Following a ketogenic diet can improve seizure management. A ketogenic diet is high in fat and very low in carbohydrates. But it can be hard to follow because there's a small range of foods allowed.
Other versions of a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet also may be helpful but not work as well. These diets include low glycemic index and Atkins diets. Experts are still studying these diets.
Surgery
If treatment with at least two antiseizure medicines doesn't work, you might have surgery to stop the seizures. Surgery works best for people who have seizures that always begin in the same place in the brain. Types of surgery include:
- Lobectomy. Surgeons find and remove the area of the brain where seizures begin.
- Thermal ablation, also called laser interstitial thermal therapy. This less invasive procedure aims highly concentrated energy at a target in the brain where seizures begin. This destroys the brain cells that cause seizures.
- Multiple subpial transection. This type of surgery involves making several cuts in areas of the brain to prevent seizures. Surgeons do this most often when they can't safely remove the area of the brain where seizures start.
- Corpus callosotomy. This surgery cuts the network of links between the neurons of the right and left halves of the brain. This is used to treat seizures that start in one half of the brain and travel to the other half. But even after surgery, seizures may still happen on the side of the brain where they started.
-
Hemispherotomy. This surgery separates one side of the brain from the rest of the brain and body. Surgeons use this type of surgery only when medicines don't manage seizures and when seizures affect only half the brain.
This surgery can cause the loss of many daily functional abilities. But children often can get those abilities back with rehabilitation.
Electrical stimulation
If surgeons can't remove or separate the area of the brain where seizures start, devices that provide electrical stimulation may help. They can work with antiseizure medicines to reduce seizures. Stimulation devices that may offer seizure relief include:
- Vagus nerve stimulation. A device placed under the skin of the chest stimulates the vagus nerve in the neck. This sends signals to the brain that lessens seizures.
- Responsive neurostimulation. Surgeons place this device on the brain or in brain tissue. The device can tell when seizure activity starts. It sends electrical stimulation to stop the seizure.
- Deep brain stimulation. Surgeons place thin wires called electrodes in certain areas of the brain to produce electrical impulses. The impulses help the body manage the brain activity that causes seizures. The electrodes attach to a pacemakerlike device placed under the skin of the chest. The device manages how much stimulation happens.
Pregnancy and seizures
People who've had seizures most often can have healthy pregnancies. But some medicines used to treat seizures sometimes can cause health conditions that are present at birth.
Valproic acid is a medicine for generalized seizures that has been linked with cognitive issues and neural tube defects, such as spina bifida, in babies. The American Academy of Neurology advises against using valproic acid during pregnancy because of risks to babies.
Talk with your healthcare professional about the risks of antiseizure medicines, including the risk of health conditions present at birth. Make a plan with your health professional before you get pregnant. Pregnancy can change medicine levels.
Some people may need to change the dosage of seizure medicine before or during pregnancy. The goal is to be on the lowest dose of the safest seizure medicine that manages seizures.
Taking folic acid before pregnancy may help prevent some complications related to taking antiseizure medicines while pregnant. Folic acid is in standard prenatal vitamins. Experts suggest that all people of childbearing age take folic acid while taking antiseizure medicines.
Birth control and antiseizure medicines
Some antiseizure medicines keep birth control from working as well. Check with your healthcare professional to see whether your medicine affects your birth control. You may need to try other forms of birth control.
You see, an epileptic seizure is an abnormal electrical disturbance of the brain. The device is implanted under the skin, and four electrodes are attached to the outer layers of your brain. The device monitors brain waves, and when it senses abnormal electrical activity it fires electrical stimulation and stops the seizures.
Potential future treatments
Researchers study other therapies that might treat seizures. These include therapies to stimulate the brain without surgery.
One area of research showing promise is MRI-guided focused ultrasound. The therapy involves pointing ultrasound beams, which are sound waves, to an area of the brain that's causing seizures. The beam creates energy to destroy brain tissue without surgery.
This type of therapy can reach deeper brain structures. It also can focus on a target without damaging the nearby tissue.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Here are some steps you can take to help manage seizures:
- Take medicine correctly. Don't change the dose without first talking with your healthcare professional. If you think that your medicine needs a change, always talk with your health professional.
- Get enough sleep. Lack of sleep can trigger seizures. Be sure to get enough rest every night.
- Wear a medical alert bracelet. This will help emergency responders know how to treat you if you have a seizure.
- Be active. Exercising and being active may help keep you healthy and reduce depression. Make sure to drink enough water. And rest if you get tired during exercise.
- Make healthy life choices. Managing stress, limiting alcohol use and not smoking all are part of a healthy lifestyle.
Personal safety
Seizures don't often result in serious injury. But if you have repeated seizures, you might injure yourself. These steps can help you avoid injury during a seizure:
- Take care near water. Don't swim alone or ride in a boat without someone nearby.
- Wear a helmet. Wear a helmet during activities such as bike riding or playing sports.
- Take showers. Don't take baths unless someone is near you.
- Soften your home. Pad sharp corners, buy furniture with rounded edges and choose chairs that have arms to keep you from falling off. Think about having carpet with thick padding to protect you if you fall.
- Don't work high up. And don't use heavy machinery.
- Have a list of seizure first-aid tips. Put them in a place where people can see them. Include phone numbers people might need if you have a seizure.
-
Consider a seizure detection device. In the U.S., the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has cleared a watchlike device that can tell when a tonic-clonic seizure is about to happen (EpiMonitor). The device alerts loved ones or caregivers so that they can check on you and make sure you're safe.
Another FDA-approved device attaches to a muscle in the arm called the bicep to watch for seizure activity (Brain Sentinel SPEAC). Talk with your healthcare professional to see if using this type of device might be right for you.
Seizure first aid
It's helpful to know what to do if you see someone having a seizure. If you're at risk of having seizures, give this information to family, friends and co-workers. Then they'll know what to do if you have a seizure.
To help someone during a seizure, take these steps:
- Carefully roll the person onto one side.
- Place something soft under the person's head.
- Loosen tight neckwear.
- Don't put your fingers or other objects in the person's mouth.
- Don't try to restrain the person.
- Clear away dangerous objects if the person is moving.
- Stay with the person until medical help arrives.
- Watch the person closely so that you can tell medical helpers what happened.
- Time the seizure.
- Stay calm.
Coping and support
Stress due to living with a seizure condition can affect your mental health. Talk with your healthcare professional about your feelings. Look for ways to find help.
At home
Your family members can provide support you may need. Tell them what you know about your seizures. Let them know they can ask you questions. Ask them about their worries. Help family members learn about your condition. Share materials or other resources that your healthcare professional gives you.
At work
Talk with your supervisor about your seizures and how they affect you. Discuss what you need your supervisor or co-workers to do if you have a seizure at work. Talk with your co-workers about seizures. This will help them understand and give you more support.
You're not alone
Reach out to family and friends. Ask your healthcare professional about local support groups or join an online support community. Don't be afraid to ask for help. Having a strong support system is vital to living with any medical condition.
Preparing for your appointment
Sometimes seizures need medical help right away. So there's not always time to prepare for an appointment.
But you may see your primary healthcare professional or be sent to a specialist. You might see a specialist trained in brain and nervous system conditions, called a neurologist. Or you might see a neurologist trained in epilepsy, known as an epileptologist.
Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment.
What you can do
- Write down what you remember about the seizure. Include when and where it happened, symptoms you had and how long it lasted, if you know. Ask anyone who saw the seizure to help you fill in the details.
- Be aware of any restrictions before your appointment. When you make the appointment, ask if there's anything you need to do ahead of time to be ready for medical tests or exams.
- Write down key personal information, including any major stresses or recent life changes.
- Make a list of all medicines, vitamins or supplements that you take, including doses.
- Take a family member or friend to your appointment. Someone who's with you can help you remember all the information you get. And the person who goes with you may be able to answer questions about your seizure that you can't.
- Write down questions to ask your healthcare professional. Making a list of questions can help you make the most of your time during your visit.
For seizures, some basic questions to ask include:
- What do you think caused my seizure?
- What tests do I need?
- What treatment do you suggest?
- How likely is it that I might have another seizure?
- How can I make sure that I don't hurt myself if I have another seizure?
- I have other health conditions. How can I best manage them together?
- Are there restrictions that I need to follow?
- Are there brochures or other printed material that I can have? What websites do you suggest?
Be sure to ask all the questions you have.
What to expect from your doctor
A healthcare professional is likely to ask you questions, such as:
- Can you describe your seizure episode?
- Was anyone there to see what happened?
- What did you feel just before the seizure? What about right after the seizure?
- Have you had a seizure or other neurological condition in the past?
- Do you have any family members who have been diagnosed with a seizure condition or epilepsy?
- Have you recently traveled outside the country?
Nov. 01, 2024