Mayo Clinic's approach to prostatectomy
 Answers to your questions
Answers to your questions
At Mayo Clinic, your doctor takes the time to listen to your questions and explain your options for prostatectomy.
A comprehensive, personalized approach
Having surgery is a highly personal experience. At Mayo Clinic, your healthcare professional listens to your concerns and issues. Together, you talk about all options and approaches to prostatectomy. Your healthcare professional answers your questions and designs a plan of care that matches your unique needs. Mayo Clinic's extensive experience and technical capabilities with prostatectomy are brought to bear within a reassuring, people-centric setting.
 Team approach to care
Team approach to care
A Mayo Clinic surgeon discusses treatment options with colleagues.
Experience and expertise
Mayo Clinic urologic surgeons and care teams collaborate with one another on all aspects of care for prostatectomy surgery. They bring unparalleled experience and expertise together for each person's benefit.
Mayo Clinic urologists have been performing radical prostatectomy procedures for several decades. Each year, more than 1,500 people choose to have these procedures at Mayo Clinic. Research suggests that surgical outcomes are directly linked to the number of procedures a surgeon has performed.
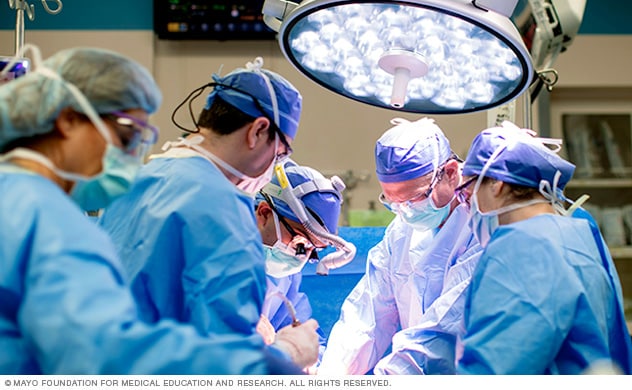 Experienced surgeons
Experienced surgeons
Mayo Clinic surgeons have vast experience in all forms of prostatectomy, performing a high volume of procedures each year.
Advanced technology and treatment options
Mayo Clinic surgeons are experts in all types of radical prostatectomy, including robot-assisted prostatectomy. Mayo Clinic surgeons pioneered the use of robot-assisted prostatectomy surgery and have been successfully performing and advancing this surgery for many years.
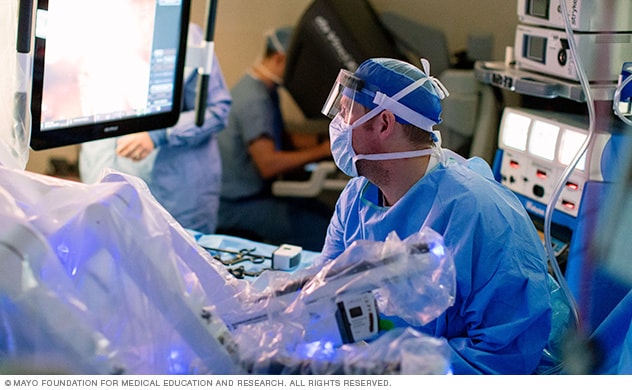 Robot-assisted prostatectomy
Robot-assisted prostatectomy
While a surgical team assists at the operating table, a Mayo Clinic surgeon sits at a remote console and uses robotic arms to conduct robot-assisted prostatectomy.
Using instruments attached to a robot during laparoscopic surgery helps the surgeon make more-precise movements with surgical tools than is possible with traditional laparoscopic surgery.
Mayo Clinic surgeons have been performing and perfecting the radical prostatectomy procedure for decades, both in open and robot-assisted forms. They also have contributed significant advances in the understanding of robotic prostatectomy technology and techniques.
Research and innovation
Mayo Clinic researchers are actively involved in studying long-term outcomes after radical prostatectomy. For decades, Mayo Clinic has been compiling a database from records of people who have had prostate cancer surgery. Through this database, Mayo Clinic doctors and researchers track treatments and outcomes, helping them develop techniques that offer you the best chance for a cancer cure and optimal quality of life.
The Mayo Clinic experience and patient stories
Our patients tell us that the quality of their interactions, our attention to detail and the efficiency of their visits mean health care like they've never experienced. See the stories of satisfied Mayo Clinic patients.

2-for-1 surgery: Hernia repair and prostate cancer removal
Bruce Simones has worn many hats in his life and likes to be busy. He's been a student, father, nurse, business owner, mentor, friend, grandfather and volunteer. Today, the 74-year-old La Crosse, Wisconsin, retiree fills his days playing golf, spending time with his family and hiking his active dogs in the Hixton Forest. He also volunteers at a warming shelter for people who are homeless and delivers furniture to families in need with a nonprofit…
Expertise and rankings
Mayo Clinic urologic surgeons and care teams leverage their decades of experience and expertise as well as research advancement to make sure people having prostatectomy surgery have the best possible outcomes.
Experience and expertise
Mayo Clinic urologists have been performing radical prostatectomy procedures for several decades. In fact, on average Mayo surgeons perform more than 1,500 of these procedures each year. Research shows that doctors who perform many prostate surgeries and work in medical centers that care for many people undergoing prostate surgery generally provide superior outcomes.
Comprehensive cancer center
Mayo Clinic Comprehensive Cancer Center meets strict standards for a National Cancer Institute comprehensive cancer center, which recognizes scientific excellence and a multidisciplinary approach to cancer prevention, diagnosis and treatment.
Nationally recognized expertise
Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota, Mayo Clinic in Jacksonville, Florida, and Mayo Clinic in Phoenix/Scottsdale, Arizona, are ranked among the Best Hospitals for cancer and urology by U.S. News & World Report.
Locations, travel and lodging
Mayo Clinic has major campuses in Phoenix and Scottsdale, Arizona; Jacksonville, Florida; and Rochester, Minnesota. The Mayo Clinic Health System has dozens of locations in several states.
For more information on visiting Mayo Clinic, choose your location below:
Costs and insurance
Mayo Clinic works with hundreds of insurance companies and is an in-network provider for millions of people.
In most cases, Mayo Clinic doesn't require a physician referral. Some insurers require referrals or may have additional requirements for certain medical care. All appointments are prioritized on the basis of medical need.
Learn more about appointments at Mayo Clinic.
Please contact your insurance company to verify medical coverage and to obtain any needed authorization prior to your visit. Often, your insurer's customer service number is printed on the back of your insurance card.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies of tests and procedures to help prevent, detect, treat or manage conditions.
Sept. 07, 2024