Overview
Hair loss (alopecia) can affect just your scalp or your entire body, and it can be temporary or permanent. It can be the result of heredity, hormonal changes, medical conditions or a normal part of aging. Anyone can lose hair on their head, but it's more common in men.
Baldness typically refers to excessive hair loss from your scalp. Hereditary hair loss with age is the most common cause of baldness. Some people prefer to let their hair loss run its course untreated and unhidden. Others may cover it up with hairstyles, makeup, hats or scarves. And still others choose one of the treatments available to prevent further hair loss or restore growth.
Before pursuing hair loss treatment, talk with your doctor about the cause of your hair loss and treatment options.
Products & Services
Symptoms
Male-pattern baldness
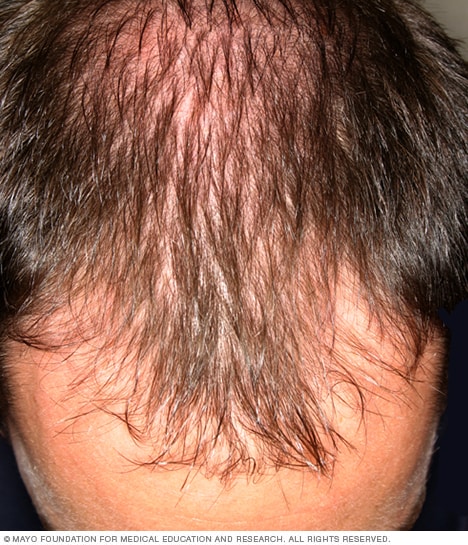
Male-pattern baldness
Male-pattern baldness typically appears first at the hairline or top of the head. It can progress to partial or complete baldness.
Female-pattern baldness
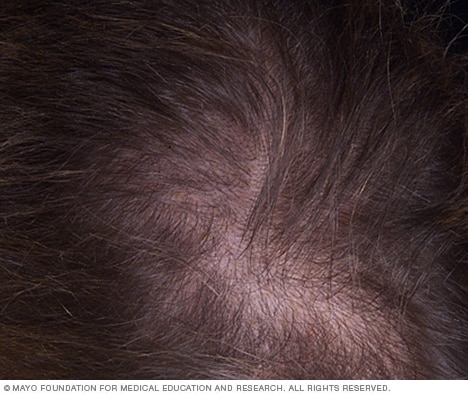
Female-pattern baldness
Female-pattern baldness typically starts with scalp hairs becoming progressively less dense. Many women first experience hair thinning and hair loss where they part their hair and on the top-central portion of the head.
Patchy hair loss (alopecia areata)
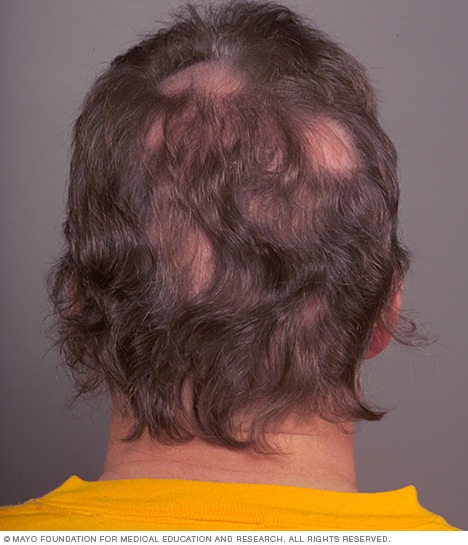
Patchy hair loss (alopecia areata)
In the type of patchy hair loss known as alopecia areata, hair loss occurs suddenly and usually starts with one or more circular bald patches that may overlap.
Traction alopecia
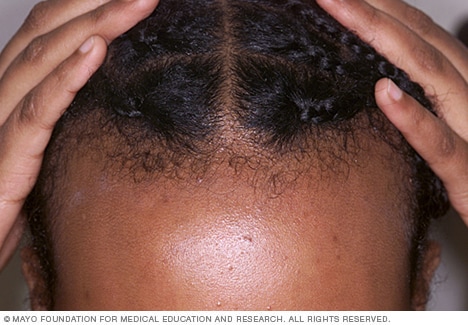
Traction alopecia
Hair loss can occur if you wear pigtails, braids or cornrows, or use tight hair rollers. This is called traction alopecia.
Frontal fibrosing alopecia
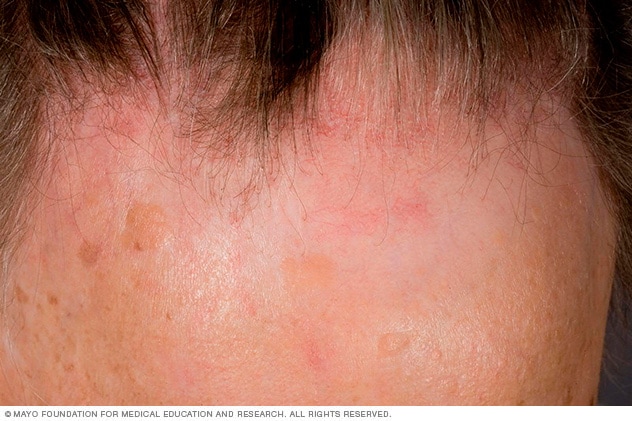
Frontal fibrosing alopecia
Early treatment of a receding hairline (frontal fibrosing alopecia) might help avoid significant permanent baldness. The cause of this condition is unknown, but it primarily affects older women.
Hair loss can appear in many different ways, depending on what's causing it. It can come on suddenly or gradually and affect just your scalp or your whole body.
Signs and symptoms of hair loss may include:
- Gradual thinning on top of head. This is the most common type of hair loss, affecting people as they age. In men, hair often begins to recede at the hairline on the forehead. Women typically have a broadening of the part in their hair. An increasingly common hair loss pattern in older women is a receding hairline (frontal fibrosing alopecia).
- Circular or patchy bald spots. Some people lose hair in circular or patchy bald spots on the scalp, beard or eyebrows. Your skin may become itchy or painful before the hair falls out.
- Sudden loosening of hair. A physical or emotional shock can cause hair to loosen. Handfuls of hair may come out when combing or washing your hair or even after gentle tugging. This type of hair loss usually causes overall hair thinning but is temporary.
- Full-body hair loss. Some conditions and medical treatments, such as chemotherapy for cancer, can result in the loss of hair all over your body. The hair usually grows back.
- Patches of scaling that spread over the scalp. This is a sign of ringworm. It may be accompanied by broken hair, redness, swelling and, at times, oozing.
When to see a doctor
See your doctor if you are distressed by persistent hair loss in you or your child and want to pursue treatment. For women who are experiencing a receding hairline (frontal fibrosing alopecia), talk with your doctor about early treatment to avoid significant permanent baldness.
Also talk to your doctor if you notice sudden or patchy hair loss or more than usual hair loss when combing or washing your or your child's hair. Sudden hair loss can signal an underlying medical condition that requires treatment.
Causes
People typically lose 50 to 100 hairs a day. This usually isn't noticeable because new hair is growing in at the same time. Hair loss occurs when new hair doesn't replace the hair that has fallen out.
Hair loss is typically related to one or more of the following factors:
- Family history (heredity). The most common cause of hair loss is a hereditary condition that happens with aging. This condition is called androgenic alopecia, male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness. It usually occurs gradually and in predictable patterns — a receding hairline and bald spots in men and thinning hair along the crown of the scalp in women.
- Hormonal changes and medical conditions. A variety of conditions can cause permanent or temporary hair loss, including hormonal changes due to pregnancy, childbirth, menopause and thyroid problems. Medical conditions include alopecia areata (al-o-PEE-she-uh ar-e-A-tuh), which is immune system related and causes patchy hair loss, scalp infections such as ringworm, and a hair-pulling disorder called trichotillomania (trik-o-til-o-MAY-nee-uh).
- Medications and supplements. Hair loss can be a side effect of certain drugs, such as those used for cancer, arthritis, depression, heart problems, gout and high blood pressure.
- Radiation therapy to the head. The hair may not grow back the same as it was before.
- A very stressful event. Many people experience a general thinning of hair several months after a physical or emotional shock. This type of hair loss is temporary.
- Hairstyles and treatments. Excessive hairstyling or hairstyles that pull your hair tight, such as pigtails or cornrows, can cause a type of hair loss called traction alopecia. Hot-oil hair treatments and permanents also can cause hair to fall out. If scarring occurs, hair loss could be permanent.
Risk factors
A number of factors can increase your risk of hair loss, including:
- A family history of balding on your mother's or father's side
- Age
- Significant weight loss
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and lupus
- Stress
- Poor nutrition
Prevention
Most baldness is caused by genetics (male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness). This type of hair loss is not preventable.
These tips may help you avoid preventable types of hair loss:
- Be gentle with your hair. Use a detangler and avoid tugging when brushing and combing, especially when your hair is wet. A wide-toothed comb might help prevent pulling out hair. Avoid harsh treatments such as hot rollers, curling irons, hot-oil treatments and permanents. Limit the tension on hair from styles that use rubber bands, barrettes and braids.
- Ask your doctor about medications and supplements you take that might cause hair loss.
- Protect your hair from sunlight and other sources of ultraviolet light.
- Stop smoking. Some studies show an association between smoking and baldness in men.
- If you're being treated with chemotherapy, ask your doctor about a cooling cap. This cap can reduce your risk of losing hair during chemotherapy.
Jan. 19, 2024