Diagnosis
Upper endoscopy
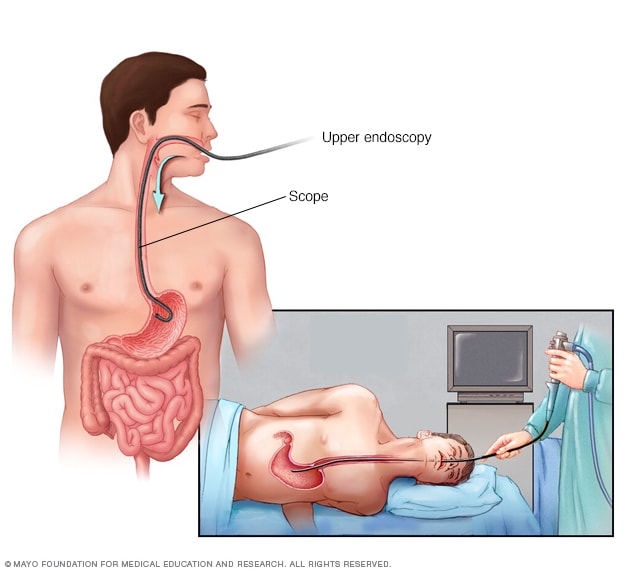
Upper endoscopy
During an upper endoscopy, a healthcare professional inserts a thin, flexible tube equipped with a light and camera down the throat and into the esophagus. The tiny camera provides a view of the esophagus, stomach and the beginning of the small intestine, called the duodenum.
Your health care provider will consider both your symptoms and test results to diagnose eosinophilic esophagitis. This will include determining whether you have gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Tests to diagnose eosinophilic esophagitis include:
- Upper endoscopy. Your provider will use a long, narrow tube (endoscope) containing a light and tiny camera and insert it through your mouth down the esophagus. The lining of your esophagus will be inspected for inflammation and swelling, horizontal rings, vertical furrows, narrowing (strictures), and white spots. Some people with eosinophilic esophagitis will have an esophagus that looks typical.
- Biopsy. During an endoscopy, a biopsy of your esophagus will be done. A biopsy involves taking a small bit of tissue. Multiple tissue samples will likely be taken from your esophagus and then examined under a microscope for eosinophils.
- Blood tests. If eosinophilic esophagitis is suspected, you may undergo some additional tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests look for the sources of your allergic reaction, also called allergens. You may be given blood tests to look for higher than usual eosinophil counts or total immunoglobulin E levels, suggesting an allergy.
- Esophageal sponge. This test is performed in the health care provider's office. It involves swallowing a capsule attached to a string. The capsule will dissolve in your stomach and release a sponge that the provider will pull out of your mouth with the string. As the sponge is pulled out, it will sample the esophageal tissues. This allows your provider to determine the degree of inflammation in your esophagus without an endoscopy.
Treatment
Eosinophilic esophagitis is considered a chronic relapsing disease, meaning that most people will require ongoing treatment to control their symptoms. Treatment will involve one or more of the following:
Dietary therapy
Depending on your response to tests for food allergies, your health care provider may recommend that you stop eating certain foods. Cutting out some foods, such as dairy or wheat products, may help to relieve symptoms and reduce inflammation. Sometimes, it may be recommended to limit your diet even more.
Medication
- Proton pump inhibitor (PPI). Your provider will likely first prescribe an acid blocker such as a PPI. This treatment is the easiest to use, but most people's symptoms don't improve.
- Topical steroid. If you do not respond to the PPI, your provider will then likely prescribe a steroid, such as fluticasone or budesonide. This steroid is in a liquid form that is swallowed to treat eosinophilic esophagitis. This type of steroid is not absorbed into the bloodstream, so you are unlikely to have the typical side effects often associated with steroids.
- Monoclonal antibodies. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently approved dupilumab (Dupixent) for treatment of adults and children 12 years and older with eosinophilic esophagitis. Dupilumab is a type of medicine known as a monoclonal antibody. It works to block the action of certain proteins in the body that cause inflammation. Dupilumab is given weekly via injection.
Dilation
If you experience severe narrowing, known as a stricture, of your esophagus, your provider may recommend dilation. Dilation, also called stretching, can help make swallowing easier. Dilation may be used if steroids are not helpful. Or dilation may be a choice to avoid ongoing use of medication.
Clinical trials
Explore Mayo Clinic studies testing new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and home remedies
If you often have heartburn, these lifestyle changes may help reduce the frequency or severity of symptoms:
- Maintain a healthy weight. Excess pounds put pressure on your belly, pushing up your stomach and causing acid to back up into your esophagus. If your weight is at a healthy level, work to maintain it. If you are overweight or obese, work to slowly lose weight — no more than 1 or 2 pounds (0.5 to 1 kilogram) a week. Ask your provider for help in creating a weight-loss strategy that will work for you.
- Avoid foods and drinks that trigger heartburn. Common triggers, such as fatty or fried foods, tomato sauce, alcohol, chocolate, mint, garlic, onion, and caffeine, may make heartburn worse. Avoid foods that you know will trigger your heartburn.
- Elevate the head of your bed. If you regularly experience heartburn at night or while trying to sleep, put gravity to work for you. Place wood or cement blocks under the feet of your bed so that the head end is raised by 6 to 9 inches (152 to 228 millimeters). If it's not possible to elevate your bed, insert a wedge between your mattress and box spring to elevate your body from the waist up.
Preparing for your appointment
If you think you have eosinophilic esophagitis, you're likely to start by seeing your regular health care provider. Your provider may recommend that you see a specialist in treating digestive diseases (gastroenterologist) or an allergist.
Because appointments can be brief, and because there's often a lot of ground to cover, it's a good idea to be well prepared. Here's some information to help you get ready, and what to expect.
What you can do
- Be aware of any pre-appointment restrictions. At the time you make the appointment, be sure to ask if there's anything you need to do in advance, such as restrict your diet.
- Bring test results. If you are seeing a new specialist after you've had an endoscopy from another provider, bring the results with you.
- Write down any symptoms you're experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment.
- Write down key personal information, including any major stresses or recent life changes.
- Make a list of all medications, vitamins or supplements that you're taking.
- Consider taking a family member or friend along. Sometimes it can be difficult to absorb all the information provided during an appointment. Someone who accompanies you may remember something that you missed or forgot.
- Write down questions to ask your provider.
Your appointment time is limited, so preparing a list of questions can help you make the most of it. For eosinophilic esophagitis, some basic questions to ask include:
- What is likely causing my symptoms?
- What kinds of tests do I need?
- Do I need an endoscopy?
- Is my condition likely temporary or chronic?
- What is the best course of action?
- What are the alternatives to the primary approach that you're suggesting?
- I have other health conditions. How can I best manage them together?
- Are there any restrictions I need to follow?
- Should I see a specialist? What will it cost?
- Is there a generic alternative to the medicine you're prescribing for me?
- Are there brochures or other printed material I can take with me? What websites do you recommend?
- Should I schedule a follow-up visit?
In addition to the questions you've prepared, don't hesitate to ask other questions during your appointment.
What to expect from your doctor
Your provider is likely to ask you a number of questions. Being ready to answer them may allow more time later to cover points you want to address.
- What are your symptoms?
- When did you first notice them?
- Have they been continuous or occasional?
- How severe are your symptoms?
- What, if anything, seems to improve your symptoms?
- What, if anything, appears to worsen your symptoms?
- Do your symptoms wake you up at night?
- Are your symptoms worse after meals or after lying down?
- Do you have difficulty swallowing?
- Have you ever had food get stuck while you are swallowing?
- Does food or sour material ever come up in the back of your throat?
- Do you have chest pain or stomach pain?
- Have you had an esophageal dilation?
- Have you been treated with a topical steroid or food elimination diet?
- Have you gained or lost weight?
- Do you experience nausea or vomiting?
- Are your symptoms worse at certain times of the year?
- Do you have asthma or any chronic respiratory disease?
- Do you have any allergies to foods or to anything in the environment, such as pollen?
- Does anyone in your family have allergies?
- Have you tried taking antacid or anti-reflux medication? What was the result?
If you're a parent of a young child, the provider also may ask if your child has trouble feeding or has been diagnosed with failure to thrive.