Overview
Blepharitis (blef-uh-RYE-tis) is a condition that causes swelling, itching and other irritation of the eyelids. Blepharitis usually affects both eyes along the edges of the eyelids.
Blepharitis may be caused by usually harmless bacteria on eyelids that become overpopulated. Another common cause is clogged oil glands of the eyelid. Other diseases or conditions may play a role in blepharitis or make it more likely to occur.
Blepharitis can't be cured, but daily care and treatments can usually control the symptoms. Blepharitis can be uncomfortable, but it usually doesn't cause permanent damage to your eyesight. It can't be passed from one person to another.

Blepharitis
Blepharitis causes the eyelids to become swollen, itchy and irritated. The eyelid may look greasy or become crusted with scales that cling to the lashes. People with blepharitis sometimes wake with their eyelids stuck together. Others may wake with dried tears around their eyes and a feeling of sand in their eyes. In this photo, the yellow around the eye is from a yellow dye sometimes used in diagnostic tests.
Symptoms
Blepharitis symptoms are typically worse in the morning. They may include:
- Swollen eyelids.
- Changes in the color of the eyelids.
- Itching or other irritation of the eyelids.
- Flaking of the skin around the eyes.
- Eyelids that appear greasy.
- Crusted eyelashes.
- Eyelids sticking together.
- Tears that appear foamy.
- Watery eyes.
- Red eyes.
- A gritty, burning or stinging sensation in the eyes.
- More frequent blinking.
- Sensitivity to light.
- Blurred vision that usually improves with blinking.
When to see a doctor
If you have blepharitis symptoms that don't improve with regular bathing or washing, make an appointment with your healthcare professional.
From Mayo Clinic to your inbox
Causes
Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids. Inflammation is the immune system's response to something it sees as a foreign substance in the body. This activity can cause swelling, irritation and other changes in the tissues of the eyelid.
Often blepharitis is caused by one of two factors. It is typical for certain bacteria to live on the surface of the eyelids and eyelashes. If this group of bacteria grows unusually, it may cause inflammation.
Pores near the base of the eyelashes release oils. Clogged oil pores may be another likely cause of blepharitis.
But the cause of blepharitis might not be known.
Risk factors
Several conditions seem to play a role or increase the risk of getting blepharitis, including:
- Dandruff of the scalp and eyebrows, also called seborrheic dermatitis.
- Bacterial disease of the eyes or eyelids.
- An inflammatory skin condition called rosacea that changes the color or appearance of skin.
- Allergies, including allergic reactions to eye medicines, contact lens solutions or eye makeup.
- An excess of eyelash mites, which are common but usually harmless.
- Tiny insects, called lice, that live on the scalp or other skin.
- Dry eyes.
Complications
Blepharitis may lead to other problems near the eyes, including:
- Eyelash problems. Blepharitis can cause your eyelashes to fall out, lose color or grow toward your eyes rather than away from them.
- Eyelid skin problems. Scarring can develop on your eyelids from long-term blepharitis. Or the eyelid edges might turn inward or outward.
- Excess tearing or dry eyes. The tear film is the substance covering the eyes and keeps the eyelids moist. Excess oil, flakes of skin or other debris can create an irregular tear film that irritates the eye, causing dryness or excess tearing.
- Stye. A stye is a painful bump on the edge of the eyelid or inside the eyelid. It's usually caused by a bacterial infection at the base of an eyelash or in an oil gland.
- Chalazion. A chalazion is a swollen bump on an eyelid caused by a blocked oil gland that causes inflammation. It usually doesn't cause pain, but it may become tender as it gets larger.
- Chronic pink eye. Blepharitis can lead to frequent cases of pink eye. Pink eye, also called conjunctivitis, is inflammation of the film over the white of the eye.
- Injury to the cornea. Constant irritation from inflamed eyelids or misdirected eyelashes can cause a sore to develop on your cornea. Not having enough tears could increase your risk of other diseases of the cornea.
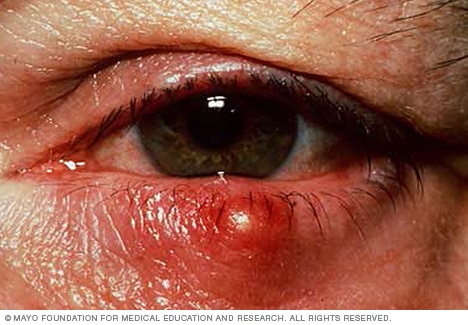
Stye
A stye is a bacterial infection involving one or more of the small glands near the base of your eyelashes. It is similar to a boil or a pimple and is often painful.

Chalazion
A chalazion is a bump on the eyelid. A chalazion occurs when a blocked oil gland becomes inflamed and swollen. Although a chalazion usually doesn't cause pain, it may become tender as it becomes more swollen. This photo shows a large chalazion on the upper eyelid and a smaller one on the lower eyelid.