Overview
Interstitial (in-tur-STISH-ul) lung disease describes a large group of disorders, most of which cause progressive scarring of lung tissue. The scarring associated with interstitial lung disease eventually affects your ability to breathe and get enough oxygen into your bloodstream.
Interstitial lung disease can be caused by long-term exposure to hazardous materials, such as asbestos. Some types of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, also can cause interstitial lung disease. In some cases, however, the causes remain unknown.
Once lung scarring occurs, it's generally irreversible. Medications may slow the damage of interstitial lung disease, but many people never regain full use of their lungs. Lung transplant is an option for some people who have interstitial lung disease.
Products & Services
Symptoms
The primary signs and symptoms of interstitial lung disease are:
- Shortness of breath at rest or aggravated by exertion
- Dry cough
When to see a doctor
By the time symptoms appear, irreversible lung damage has often already occurred. Nevertheless, it's important to see your doctor at the first sign of breathing problems. Many conditions other than interstitial lung disease can affect your lungs, and getting an early and accurate diagnosis is important for proper treatment.
Causes
Bronchioles and alveoli in the lungs
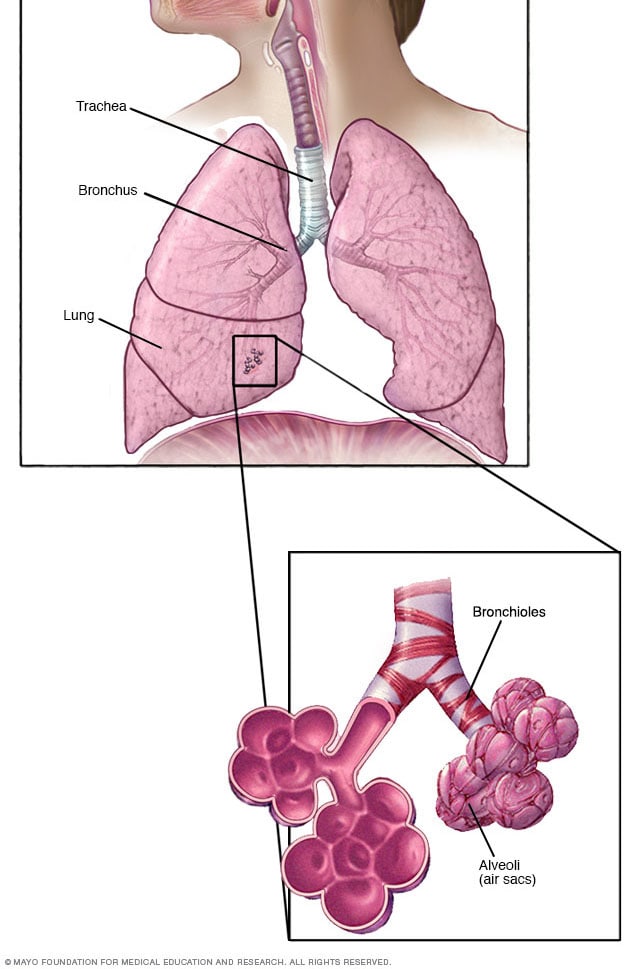
Bronchioles and alveoli in the lungs
In your lungs, the main airways, called bronchi, branch off into smaller and smaller passageways. The smallest airways, called bronchioles, lead to tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Interstitial lung disease seems to occur when an injury to your lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, your body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage. But in interstitial lung disease, the repair process goes awry and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into your bloodstream.
Interstitial lung disease can be triggered by many different things — including airborne toxins in the workplace, drugs and some types of medical treatments. In most cases, the causes are unknown.
Occupational and environmental factors
Long-term exposure to a number of toxins and pollutants can damage your lungs. These may include:
- Silica dust
- Asbestos fibers
- Grain dust
- Bird and animal droppings
- Radiation treatments
- Indoor hot tubs
Some people who receive radiation therapy for lung or breast cancer show signs of lung damage months or sometimes years after the initial treatment.
Medications
Many drugs can damage your lungs, especially:
- Chemotherapy drugs. Drugs designed to kill cancer cells, such as methotrexate (Otrexup, Trexall, others) and cyclophosphamide, can also damage lung tissue.
- Heart medications. Some drugs used to treat irregular heartbeats, such as amiodarone (Nexterone, Pacerone) or propranolol (Inderal, Innopran), may harm lung tissue.
- Some antibiotics. Nitrofurantoin (Macrobid, Macrodantin, others) and ethambutol (Myambutol) can cause lung damage.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Certain anti-inflammatory drugs, such as rituximab (Rituxan) or sulfasalazine (Azulfidine), can cause lung damage.
Medical conditions
Lung damage can also result from autoimmune diseases such as:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Scleroderma
- Dermatomyositis and polymyositis
- Mixed connective tissue disease
- Sjogren's syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
The list of substances and conditions that can lead to interstitial lung disease is long. Even so, in some cases, the causes are never found. Disorders without a known cause are grouped together under the label of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias, the most common and deadly of which is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Risk factors
Factors that may make you more susceptible to interstitial lung disease include:
- Age. Interstitial lung disease is much more likely to affect adults, although infants and children sometimes develop the disorder.
- Exposure to occupational and environmental toxins. If you work in mining, farming or construction or for any reason are exposed to pollutants known to damage your lungs, your risk of interstitial lung disease is increased.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease. If you have uncontrolled acid reflux or indigestion, you may be at increased risk of interstitial lung disease.
- Smoking. Some forms of interstitial lung disease are more likely to occur in people with a history of smoking, and active smoking may make the condition worse, especially if there is associated emphysema.
- Radiation and chemotherapy. Having radiation treatments to your chest or using some chemotherapy drugs makes it more likely that you'll develop lung disease.
Complications
Interstitial lung disease can lead to a series of life-threatening complications, including:
- High blood pressure in your lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Unlike systemic high blood pressure, this condition affects only the arteries in your lungs. It begins when scar tissue or low oxygen levels restrict the smallest blood vessels, limiting blood flow in your lungs. This in turn raises pressure within the pulmonary arteries. Pulmonary hypertension is a serious illness that becomes progressively worse.
- Right-sided heart failure (cor pulmonale). This serious condition occurs when your heart's lower right chamber (right ventricle) — which is less muscular than the left — has to pump harder than usual to move blood through obstructed pulmonary arteries. Eventually the right ventricle fails from the extra strain. This is often a consequence of pulmonary hypertension.
- Respiratory failure. In the end stage of chronic interstitial lung disease, respiratory failure occurs when severely low blood oxygen levels along with rising pressures in the pulmonary arteries and the right ventricle cause heart failure.