Overview
Parts of the immune system
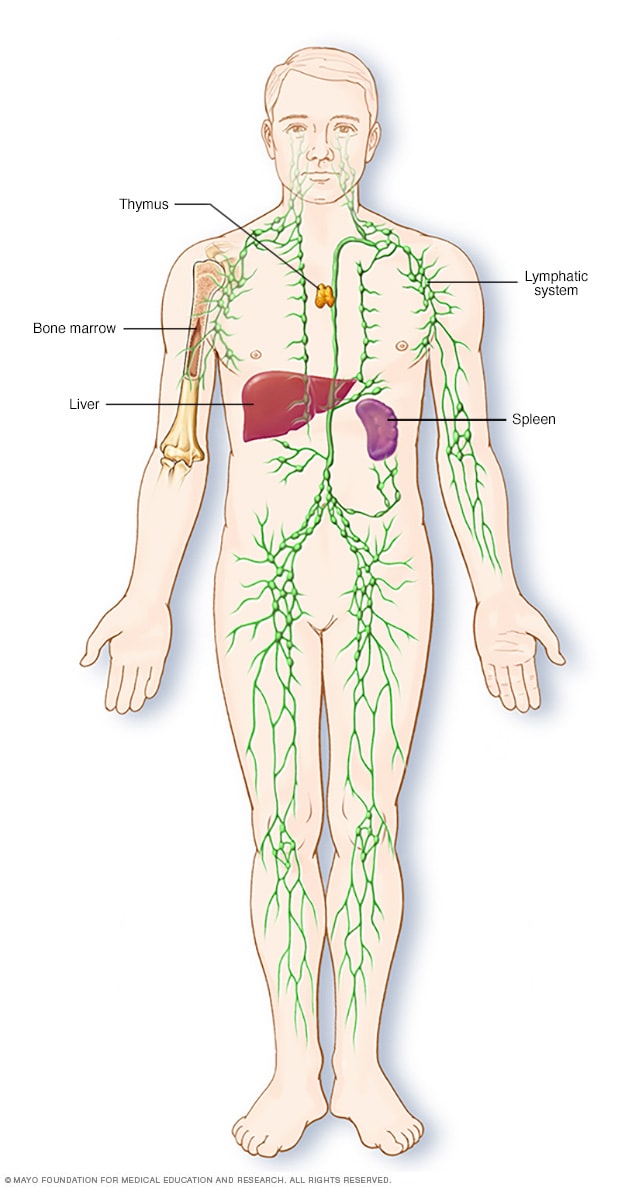
Parts of the immune system
The lymphatic system is part of the body's immune system, which protects against infection and disease. The lymphatic system includes the spleen, thymus, lymph nodes and lymph channels, as well as the tonsils and adenoids.
Lymph node clusters
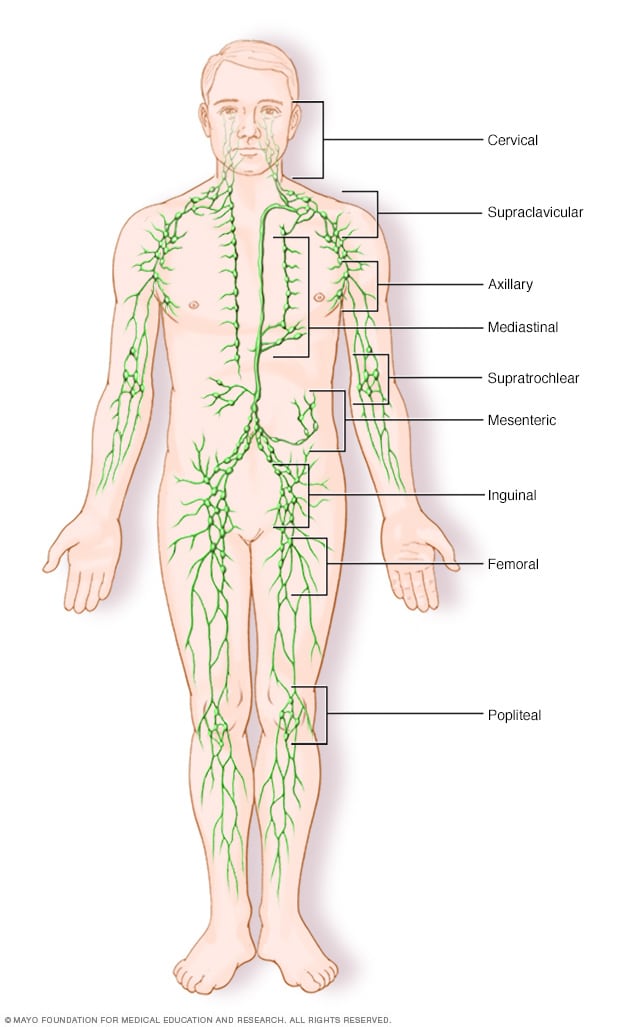
Lymph node clusters
Lymph nodes are bean-sized groups of white blood cells. Hundreds of these nodes cluster all through the lymphatic system. For instance, they're near the knees, groin, neck and armpits. A network of lymphatic vessels connects these nodes.
Hodgkin lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is part of the body's germ-fighting and disease-fighting immune system. Hodgkin lymphoma begins when healthy cells in the lymphatic system change and grow out of control.
The lymphatic system includes lymph nodes. They are found throughout the body. Most lymph nodes are in the abdomen, groin, pelvis, chest, underarms and neck.
The lymphatic system also includes the spleen, thymus, tonsils and bone marrow. Hodgkin lymphoma can affect all these areas and other organs in the body.
Hodgkin lymphoma, which used to be called Hodgkin disease, is one of two broad types of lymphoma. The other is non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Advances in diagnosis and treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma have helped give people with this disease the chance for a full recovery.
Schedule your lymphoma appointment
Dr. Rafael Fonseca, hematologist and Chief Innovation Officer at Mayo
Clinic
We are accepting new patients. Our team of experts is standing by to schedule your Hodgkin's lymphoma appointment now.
Call your preferred Mayo Clinic location:
Types
Symptoms
Swollen lymph nodes
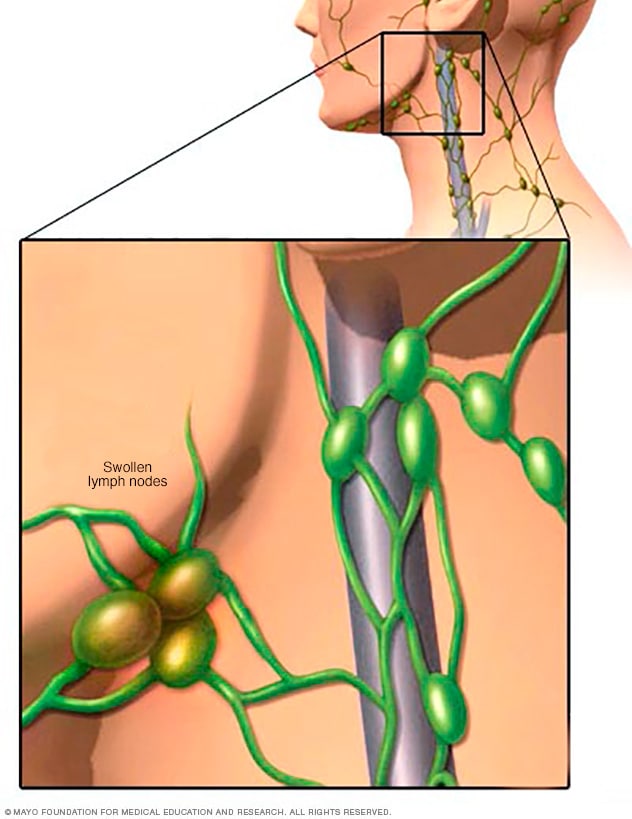
Swollen lymph nodes
One of the most common places to find swollen lymph nodes is in the neck. The inset shows three swollen lymph nodes below the lower jaw.
Signs and symptoms of Hodgkin lymphoma may include:
- Painless swelling of lymph nodes in the neck, armpits or groin.
- Fever.
- Feeling very tired.
- Night sweats.
- Weight loss that happens without trying.
- Itchy skin.
When to see a doctor
Make an appointment with a doctor or other healthcare professional if you have ongoing symptoms that worry you. Hodgkin lymphoma symptoms are like those of many more-common conditions, such as infections. The healthcare professional may check for those causes first.
Causes
Healthcare professionals aren't sure what causes Hodgkin lymphoma. It begins with changes in the DNA of a disease-fighting blood cell called a lymphocyte. A cell's DNA contains the instructions that tell the cell what to do.
The DNA changes tell the cells to multiply quickly and live when other cells would naturally die. The Hodgkin lymphoma cells attract many healthy immune system cells to protect them and help them grow. The extra cells crowd into the lymph nodes and cause swelling and other symptoms.
There are multiple types of Hodgkin lymphoma. The type of lymphoma you have is based on the characteristics of the cells involved in your disease and their behavior. The type of lymphoma you have helps determine your treatment options.
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma is the more common type of this disease. People diagnosed with this type have large lymphoma cells called Reed-Sternberg cells in their lymph nodes.
Subtypes of classical Hodgkin lymphoma include:
- Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Mixed cellularity Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Lymphocyte-depleted Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Lymphocyte-rich Hodgkin lymphoma.
Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma
This type of Hodgkin lymphoma is much rarer. It involves lymphoma cells sometimes called popcorn cells because of how they look. Usually, it is diagnosed early and may need less intensive treatments than the classical type of Hodgkin lymphoma.
Risk factors
Factors that can increase the risk of Hodgkin lymphoma include:
- Your age. Hodgkin lymphoma is most often diagnosed in people in their 20s and 30s and those over age 65.
- A family history of Hodgkin lymphoma. Having a blood relative with Hodgkin lymphoma increases the risk of Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Being male. People who are assigned male at birth are slightly more likely to develop Hodgkin lymphoma than are those who are assigned female at birth.
- Past Epstein-Barr infection. People who have had illnesses caused by the Epstein-Barr virus are at higher risk of Hodgkin lymphoma than are those who haven't. One example is infectious mononucleosis.
- HIV infection. People who are infected with HIV have an increased risk of Hodgkin lymphoma.
There's no way to prevent Hodgkin lymphoma.
Dec. 20, 2024